![]()
where,
I = current, amp
V = potential difference, volts
R = resistance, ohms
![]()
where,
ρ = resistivity or specific resistance, ohm-m
L = length of wire, m
A = cross-sectional area of wire, m2
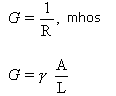
where,
γ = conductivity or specific conductance, mhos/m
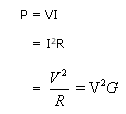
where,
P = electric power, watts
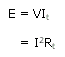
where, E = electric energy, Joules
V = potential difference, Volts
I = Current, Amperes
R = resistance, ohms
t = time, seconds
E = 0.24I2Rt, cal
For Battery

where

(i) The algebraic sum of all the currents directed towards a junction point is zero.
(ii) The algebraic sum of all the voltage rise taken in a specified direction around a closed circuit is zero.
Series Circuits:
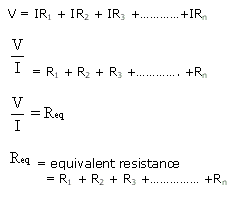
Parallel Circuits:
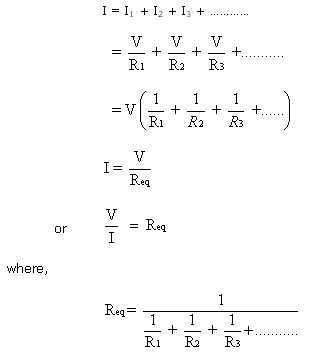
The force acting between two charged bodies q1 and q2 in air is proportional to the product of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.





0 comments:
Post a Comment