In real this is how an TRANSFORMER looks like..
the transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one end of the coil to the another coil by mutual induction method......

Introduction of transformer..
A transformer makes use of Faraday's law and the Ferromagnetic properties of an iron core to efficiently raise or lower AC voltages. It of course cannot increase power so that if the voltage is raised, the current is proportionally lowered and vice versa.
How the ideal transformer looks like
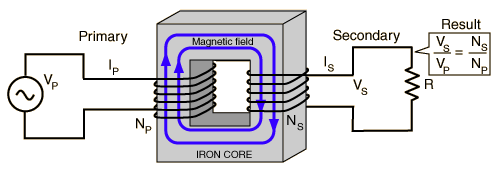
Relation between transformers & Faraday's law..
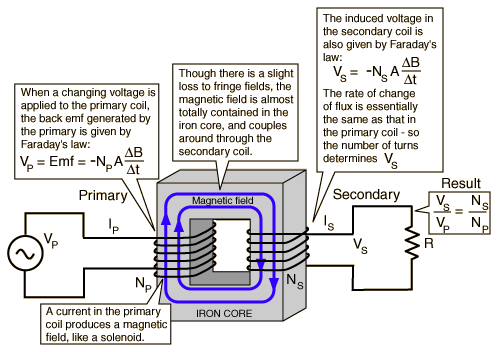
Formulas for transformers.............

Concepts of transformers...............
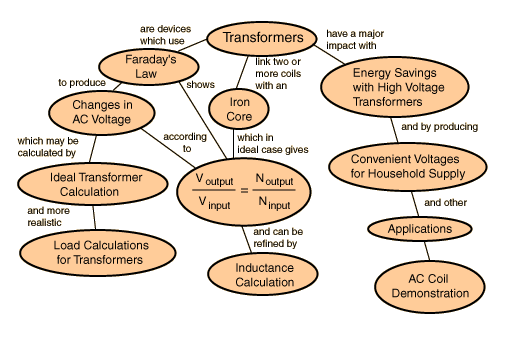
Types of transformers...
STEPUP TRANSFORMER:-

A "step-up transformer" allows a device that requires a high voltage power supply to operate from a lower voltage source. The transformer takes in the low voltage at a high current and puts out the high voltage at a low current.
STEPDOWN TRANSFORMER:-

A "step-down transformer" allows a device that requires a low voltage power supply to operate from a higher voltage. The transformer takes in the high voltage at a low current and puts out a low voltage at a high current.
Common Types of Transformer...
Following are the few common types of transformer
Power Transformer - These operate at 50 to 400 Hz at a absolute nominal line voltage from 105 to 130 V. They are actually made with single and multiple secondaries with various step-up and step-down turns ratios.
Secondary Transformer - Secondaries transformer could have a single tap, multiple taps and even sometimes no tap. Some units are prepared with a tapped primary. Output voltage could start ranging from three to several thousand volts with output currents from .01 to 1500 A.
The Cores Transformer - The cores transformers are made up of iron or steel laminations. They are packaged in a hermetically sealed case especially for military or space use or with an open frame or even plastic enclosure for commercial, consumer or any industrial use.
Isolation Transformer - These types of transformer operate with a one-to-one turn’s ratio between primary and secondary, as isolating the line from the secondary load. Usually, an isolation transformer further comprises of Faraday shield, which is in fact a screen of nonmagnetic metal wound between the primary and secondary and then connected to the transformer core.
The Shield Transformer - The shield transformer acts particularly to prevent capacitive coupling of spurious signals and sound between windings, and it as well reduces transformer efficiency by improving leakage current.
Control Transformer - These are used as small power transformer for controlling components like relays and low voltage ac control devices. Common output voltages come in 12 and 24 Vac at current capabilities of 4 to16 A.
Autotransformer - Autotransformers are types of single winding with either fixed or variable step-up or step-down turn’s rations. They are actually smaller and less pricey than the two-winding types.
Audio Transformer - These vary from the power transformer types in, which they are used to give matching electrical characteristics of an output amplifier to that of any normal load speaker. In high-fidelity audio systems, they further operate from 20 Hz to 20 KHz. This audio transformer comprises of voice communications only and operates from 200 to 500 Hz.
Radio Frequency Transformer - These radio frequency transformers operate at a fixed high frequency with a capacitor across primary, secondary or sometimes even both to create a tuned or resounding circuit. Most types normally use an air core; however some are made up of ferrite slug to allow any sort of adjustment for inductance windings over a given range. They are generally assembled in aluminum-shielded container to reduce pickup or radiation of magnetic fields.
Pulse Transformer - These types are used for the generation and transmission of square wave pulses with emphasis on fast rise and fall times of the pulse and high-frequency response. These transformers are packaged in a miniature enclosure, 1/4 inch to 1/2 inch in diameter, and use an air core.
Working of transformer................
Transformer refers to the static electromagnetic setting which can transfer power from one circuit to another one. In AC circuits, AC voltage, current and waveform can be transformed with the help of Transformers. Each transformation is usually to transfer from one circuit to another one by the way of electromagnetism, but it has no direct relation with this circuit. It also can be transformed through electromagnetism (electrical manner). This electromagnetism is known as auto-transformer.
Transformer plays an important role in electronic equipment. AC and DC voltage in Power supply equipment are almost achieved by transformer’s transformation and commutation. At the same time the electrical parameters transformed by transformer are not one but a few ones.
Most of the isolation, matching and impedance in the circuit carry out by transformer. Most of isolation, matching and impedance in the circuit carry out by transformer.Simple schematic diagram of the transformer is shown in (1-1). It is connected by closed-magnet (iron cores), two windings and AC power supply. The winding is called the primary winding; another winding is connected with load, and it is called secondary windings. 
No-load state of Transformer: viz. the disconnecting state between he secondary winding and load (Figure 1-2). Connect the primary winding and the power supply of AC voltageU1, and then it will produce alternating current I0, this current is called no-load currents. This current set up alternating magnetic flowφ0 which is closed along iron core magnetic circuit. At the same time, it traverses the primary winding and secondary winding, and then produces inducting electromotive forceE2 (secondary no-load voltage).
Circuit symbol for transformers...
 | Transformer with two windings and iron core. |
 | Step-down or step-up transformer. The symbol shows which winding has more turns, but not usually the exact ratio. |
 | Transformer with three windings. The dots show the relative configuration of the windings. |
 | Transformer with electrostatic screen preventing between the windings. |

























































